সিঙ্গলি লিংকড লিস্ট#
ইতিপূর্বের উদাহরণগুলোতে আমরা পাইথনের বিল্ট-ইন ডাটা স্ট্রাকচার - লিস্টের ব্যবহার দেখে এসেছি। লিংকড লিস্টকে আমরা সেই লিস্টের বিশেষায়িত রূপ বলতে পারি। বিশেষায়িত বলার কারণ হচ্ছে, এই লিস্টের ভিতর কিছু বিশেষ ব্যাপার-স্যাপার রয়েছে।
মোটামুটি চার টাইপের লিংকড লিস্ট রয়েছে: সিম্পল (Simple) বা সিঙ্গলি (Singly) লিংকড লিস্ট, ডাবলি (Doubly) লিংকড লিস্ট, মাল্টিপ্লাই (Multiply) লিংকড লিস্ট ও সার্কুলার (Circular) লিংকড লিস্ট। আজকে আমরা সিঙ্গলি লিংকড লিস্ট সম্পর্কে জানার চেষ্টা করব।
সহজ ভাষায়, সিঙ্গলি লিংকড লিস্ট হল কতগুলো নোডের চেইন বা সমাহার। আরেকটু পুস্তকী ভাষায় বলতে গেলে, সিঙ্গলি লিংকড লিস্ট হল কতগুলো ডাটা এলিমেন্ট বা নোডের ধারাবাহিক সংগ্রহশালা (কালেকশন - collection)। লিনিয়ার সিকুয়েন্স আর কি! এখানে, নোড আসলে একটা বেসিক ইউনিট। প্রতিটি নোডে দুটি ফিল্ড থাকে। প্রথম ফিল্ডে থাকে ডাটা আইটেম আর শেষের ফিল্ডে থাকে পয়েন্টার বা পরবর্তী নোডের লিংক।
ব্যাপারটা সহজে বোঝার জন্য আমরা শিশুবেলায় ফিরে যেতে পারি। সেই স্কুল পালানো দুরন্তপনার দিনগুলো কি মনে আছে আমাদের? বিশেষ করে, হাত ধরাধরি করে দশ-পনেরজন পাশাপাশি দাঁড়িয়ে থাকার দিনগুলো? এটা মনে থাকলেই আপাতত চলবে। যখন আমরা দশ-পনেরজন হাত ধরাধরি করে পাশাপাশি দাঁড়াতাম তখন আমরা আমাদের দু’হাত দিয়ে দুজনকে ধরতাম। একজনের ডানহাত পরবর্তী জনের বামহাত ধরত, তার ডান হাত আবার তার পরের জনের বামহাত। এভাবে একটা হিউম্যান চেইন গঠন করতাম আমরা। এই চেইনে প্রতিটি মানুষকে এক-একটি নোড হিসেবে কল্পনা করতে পারি আমরা। সেই নোডের ডাটা আইটেম আমাদের মূলদেহ আর ডানহাত হল পয়েন্টার। কি এখনো সহজ মনে হচ্ছে না? তাহলে একটা ছবি দেখা যাক।
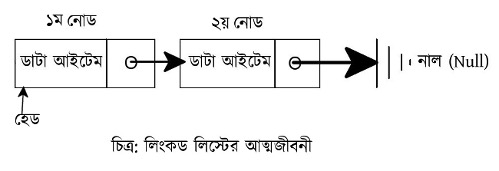
এতক্ষণ আমরা যে হাত ধরাধরির কাহিনী বর্ণনা করছিলাম, এই চিত্রটা আসলে তারই মানসচিত্র (ভিজুয়ালাইজেশন - visualization)। প্রথম নোড থেকে মূলত সিঙ্গলি লিংকড লিস্টের অগ্রযাত্রা শুরু হয়। প্রথম নোডের ডাটা আইটেম অংশে প্রথম ভ্যালুটা থাকে। প্রথম নোডের পয়েন্টার অংশ দ্বিতীয় নোডকে নির্দেশ করে। এভাবে চলতে থাকে। একটা লিস্টের পরিসমাপ্তিকে মূলত নাল (Null) রেফারেন্স দ্বারা চিহ্নিত করা হয়। অনেক সময় None পরিসমাপ্তি বুঝানো হয়। পরিসমাপ্তি দ্বারা বুঝানো হচ্ছে যে এই নোডের পরে আর কোন নোড নেই।
অপারেশন#
এক নজরে আমরা এখন সিঙ্গলি লিংকড লিস্টের সকল অপারেশন দেখব। সাধারণত নয় ধরনের ফাংশন বা মেথডের মাধ্যমে এই অপারেশনগুলো সম্পাদিত হয়।
appendleft(item)#
লিস্টের শুরুতে নতুন একটি নোড সংযোজনের মাধ্যমে নতুন কোন ডাটা আইটেম সংযোজন করার ক্ষেত্রে এই ফাংশন বা মেথডটি ব্যবহার করা হয়। আর্গুমেন্ট বা প্যারামিটার হিসেবে আলোচ্য ডাটা আইটেমটিকে গ্রহণ করলেও এটি কোন কিছু রিটার্ন করে না।
append(item)#
লিস্টের শেষে নতুন একটি নোড সংযোজনের মাধ্যমে নতুন কোন ডাটা আইটেম সংযোজন করার ক্ষেত্রে এই ফাংশন বা মেথডটি ব্যবহার করা হয়। আর্গুমেন্ট বা প্যারামিটার হিসেবে আলোচ্য ডাটা আইটেমটিকে গ্রহণ করলেও এটি কোন কিছু রিটার্ন করে না।
insert(position, item)#
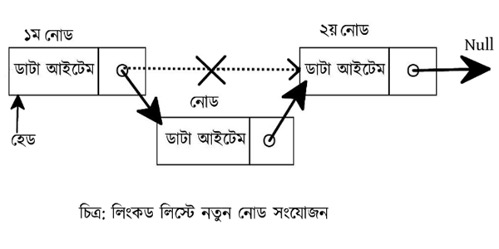
লিস্টের নির্দিষ্ট কোন অবস্থানে (পজিশানে) নতুন একটি নোড সংযোজনের মাধ্যমে নতুন কোন ডাটা আইটেম সংযোজন করার ক্ষেত্রে এই ফাংশন বা মেথডটি ব্যবহার করা হয়। আর্গুমেন্ট বা প্যারামিটার হিসেবে আলোচ্য পজিশান ও ডাটা আইটেমটিকে গ্রহণ করলেও এটি কোন কিছু রিটার্ন করে না।
remove(item)#
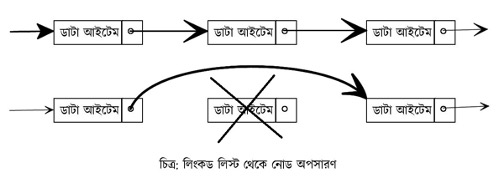
লিস্টের শুরু থেকে নির্দিষ্ট কোন ডাটা আইটেম ও সংশ্লিষ্ট নোড অপসারণ করার জন্য এই ফাংশন বা মেথডটি ব্যবহার করা হয়। আর্গুমেন্ট বা প্যারামিটার হিসেবে আইটেমটিকে গ্রহণ করলেও এটি কোন কিছু রিটার্ন করে না। (ধরে নেয়া হয়, আইটেমটি লিস্টে রয়েছে)
pop()#
সাধারণত এই ফাংশন বা মেথড লিস্টের শেষের ডাটা আইটেমটিকে ও সংশ্লিষ্ট নোড অপসারণ করে এবং ডাটা আইটেম রিটার্ন করে। (ধরে নেয়া হয়, লিস্টে অন্ততপক্ষে একটি আইটেম রয়েছে)
is_empty()#
এটি একটি বুলিয়ান ফাংশন (বা মেথড)। লিস্ট খালি কিনা সেটি চেক করে True বা False রিটার্ন করে। এর কোন প্যারামিটার নেই।
size()#
এই ফাংশন (বা মেথড) লিংকড লিস্টের মোট আইটেম (নাকি নোড?) সংখ্যা রিটার্ন করে। এরও কোন প্যারামিটার নেই।
search(item)#
এটি একটি বুলিয়ান ফাংশন (বা মেথড)। একটি আইটেমকে আর্গুমেন্ট বা প্যারামিটার হিসেবে গ্রহণ করে লিংকড লিস্টে সেটি রয়েছে কিনা তা সার্চ করে দেখে এবং True বা False রিটার্ন করে।
index(item)#
এই ফাংশন বা মেথডটি একটি আইটেমকে আর্গুমেন্ট বা প্যারামিটার হিসেবে গ্রহণ করে। তারপর সেটিকে লিংকড লিস্টে সার্চ করে দেখে এর পজিশন রিটার্ন করে। (ধরে নেয়া হয়, আইটেমটি লিস্টে রয়েছে)
printlist()#
এই ফাংশন বা মেথডটি লিস্টের সবগুলো আইটেমকে প্রিন্ট করবে। (ধরে নেয়া হয়, লিস্টে ন্যূনতম একটি আইটেম রয়েছে।)
ইমপ্লিমেন্টেশন#
স্টাক, কিউ বা ডেকের মত সিঙ্গলি লিংকড লিস্টের ইমপ্লিমেন্টেশন সরল প্রকৃতির নয়। খানিকটা জটিল হলেও পাইথনে (3.x) ভাল ধারণা থাকলে ইমপ্লিমেন্ট করতে কষ্ট হবার কথা নয়। আসলে ডাটা স্ট্রাকচার বা অ্যালগরিদম দেখে ইমপ্লিমেন্ট করার মত কোন বিষয় নয়। কি হচ্ছে বা কি হবে তা সম্পর্কে স্পষ্ট ধারণা থাকলে সহজেই কোড লিখে ফেলা যায়। তারপরও উদাহরণ হিসেবে এটা দেখা যেতে পারে:
class Node():
"""
@description: This class will act as node for Linked List and will hold data.
@params:
item: item means data item
next_node: a pointer, indicates the address of next node
"""
def __init__(self, item=None, next_node=None):
self.item = item
self.next_node = next_node
class SinglyLinkedList():
"""
@description: This class defines several methods for Singly Linked List.
@params:
head: indicates the first node of list
"""
def __init__(self, head=None):
self.head = head
def appendleft(self, item):
# adds an item to the head of the list
new_node = Node(item)
new_node.next_node = self.head
self.head = new_node
def append(self, item):
# adds an item to the end of the list
current = self.head
if current:
while current.next_node:
current = current.next_node
current.next_node = Node(item)
else:
self.head = Node(item)
def insert(self, position, item):
# adds an item to an exact position of the list
if position == 0:
self.appendleft(item)
print(item, "inserted to position", position)
elif position == self.size():
self.append(item)
print(item, "inserted to position", position)
elif position > self.size():
print("Index out of range")
else:
current = self.head
index = 0
while current:
if index != position:
previous = current
current = current.next_node
index += 1
else:
new_node = Node(item, current)
previous.next_node = new_node
current = False
print(item, "inserted to position", position)
def is_empty(self):
# checks whether the list is empty or not
if self.head == None:
return True
else:
return False
def size(self):
# returns the total items number of the list
current = self.head
count = 0
while current:
count += 1
current = current.next_node
return count
def index(self, item):
# returns the index position of an item in the list
current = self.head
index = 0
while current:
if current.item == item:
return index
else:
current = current.next_node
index += 1
return None
def search(self, item):
# checks whether an item exist in the list or not
current = self.head
found = False
while current and not found:
if current.item == item:
found = True
else:
current = current.next_node
if current is None:
print("Item not found")
return found
def popleft(self):
# removes the first item of the list
if self.is_empty():
print("Empty list")
else:
current = self.head
temp = current.item
self.head = current.next_node
del current
return temp
def pop(self):
# removes the last item of the list
if self.is_empty():
print("Empty list")
else:
current = self.head
previous = None
while current.next_node:
previous = current
current = current.next_node
if current == self.head:
self.head = None
else:
previous.next_node = None
temp = current.item
del current
return temp
def remove(self, item):
# removes an item from the listot
if self.is_empty():
print("Empty list")
else:
current = self.head
previous = None
found = False
while current and not found:
if current.item == item:
found = True
else:
previous = current
current = current.next_node
if current is None:
print("Item not found")
elif previous is None:
self.popleft()
print(item, "removed")
else:
temp = current.next_node
del current
print(item, "removed")
previous.next_node = temp
def printlist(self):
if self.is_empty():
print("Empty list")
else:
current = self.head
print(current.item)
while current.next_node:
current = current.next_node
print(current.item)
def main():
# defining the main function for the singly linked list
mylist = SinglyLinkedList()
# mylist is an object of SinglyLinkedList class
while True:
print("1. Append to Left \n2. Append \n3. Insert \n4. Get Size \n5. Search \n6. Get Index \n7. Remove \n8. Pop from Left \n9. Pop \n10. Print List \n11. Quit")
print("\nWhat do you wanna do now?")
case = int(input())
# starting something, equivalent to Switch statement in C/C++
if case == 1:
# in this case, we will call our appendleft method
print("Input item, you wanna append to left of list:")
item = input()
mylist.appendleft(item)
print("Congrats!", item, "has been added.")
elif case == 2:
# in this case, we will call our appendleft method
print("Input item, you wanna append to list:")
item = input()
mylist.append(item)
print("Congrats!", item, "has been appended.")
elif case == 3:
# in this case, we will call our appendleft method
print("Input position:")
position = int(input())
print("Input item, you wanna push to list:")
item = input()
mylist.insert(position, item)
elif case == 4:
# in this case, we will call our size method
print("There are", mylist.size(), "items in the list.")
elif case == 5:
# in this case, we will call our search method
print("Input item, you wanna search in list:")
item = input()
print(mylist.search(item))
elif case == 6:
# in this case, we will call our insert method
print("Input item, you wanna know its index:")
item = input()
index = mylist.index(item)
print(item, "is in index number", index)
elif case == 7:
# in this case, we will call our remove method
if mylist.is_empty():
print("Empty list")
else:
print("Input item, you wanna remove:")
item = input()
mylist.remove(item)
elif case == 8:
# in this case, we will call our pop method without position
if mylist.is_empty():
print("Empty list")
else:
item = mylist.popleft()
print(item, "removed")
elif case == 9:
# in this case, we will call our pop method without position
if mylist.is_empty():
print("Empty list")
else:
item = mylist.pop()
print(item, "removed")
elif case == 10:
# in this case, we will print our list
if mylist.is_empty():
print("Empty list")
else:
mylist.printlist()
elif case == 11:
# in this case, we will quit our script
print("The script is gonna quit.")
quit()
else:
print("Oops! Wrong Choice.")
main()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()অদূর ভবিষ্যতে আমরা ডাবলি (Doubly) লিংকড লিস্ট ও সার্কুলার (Circular) লিংকড লিস্ট সম্পর্কেও জানব। তবে তার আগে সিঙ্গলি লিংকড লিস্টে হাত পাকাতে হবে আমাদের। সেজন্য সিঙ্গলি লিংকড লিস্ট ব্যবহার করে আমরা স্টাক ও কিউ ইমপ্লিমেন্ট করব। আর হ্যাকারর্যাংক ও হ্যাকারআর্থ-এর কিছু প্রব্লেম সলভ করব।